- Lectures - online | onsite
- Practicals
- Assignments
- Assessments
Lecture 1: Topographic Mapping
J Mwaura
Mode of delivery
Course Outline
- Concepts, theories and principles of large scale topographic mapping.
- Planning and design: budgeting, implementation, production.
- Use of digital maps.
- Large-scale base mapping: approach; control and field data gathering.
- Field completion, equipment and products.
- Contemporary trends.
What is topographic mapping?
Concepts
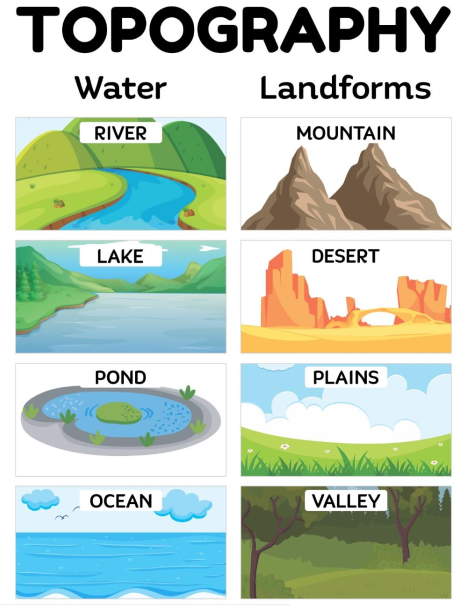
What is topography?
- the study of the land surface
- The topography of an area refers to the surface shapes and features on the ground and their arrangement
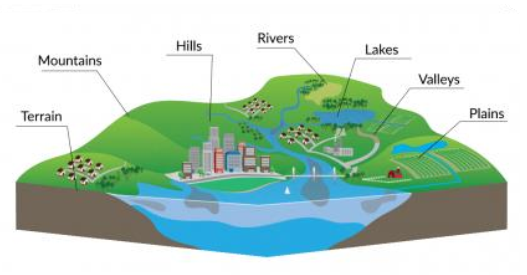
Definitions - What is?
Survey
- The science, art, and profession of determining the positions of points on the surface of the earth and measuring the distances, directions, angles, and elevations between them
Mapping
- The process of creating a visual representation of the data gathered during survey, which can take many forms, from simple 2D plans to complex 3D models and geographic information systems (GIS) that integrate multiple layers of data
Cartography
- The profession of making maps
Definitions - What is?
Topographic survey & mapping
- A topographic survey gathers data about the natural and man-made features of the land, as well as its terrain
- Permanent features such as buildings, fences, trees and streams accurately define the ground and its boundaries
- Land contours and spot levels show the elevation of the terrain
Topographic map
Site topography
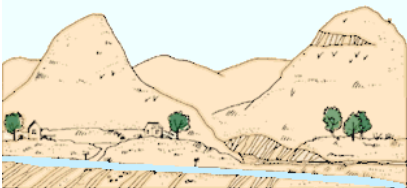
Topographic map
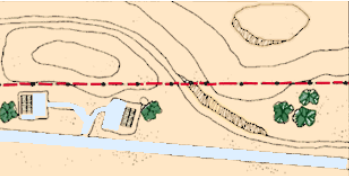
Topographic map
A topographic map is a graphic representation to scale, showing horizontal and vertical topographic features of come portion of the earth's surface, systematically plotted on a plane surface
Why a topographic map? - Purpose
Purpose
Topographic surveys are conducted for;
- To show natural & physical features on the ground
- To depict the difference in height between land forms

Topographic map?
- Is thus, a product of both engineering and graphic arts
Why topographic mapping?
Natural and human activities on earth

Who uses a topographic map?
Use
Topographic maps are used to accurately visualise their sites and help bring forward development by
- architects
- engineers
- building contractors and others
Topographic surveys supports;
- Planning
- Engineering & design
- Construction, and
- Environmental restoration activities
Topographic survey process
Topo survey workflow
Ground control surveys
- GNSS technology
- Triangulation or Traversing
Data collection such as features of interest
- LiDAR
- GNSS
Field verification
- Field verification
Large-scale Topo survey. How?
A typical topographical survey process includes;
- Gathering information, i.e. the geographical area to be included, the level of detail, accuracy and data output
- Planning & pricing - schedule time & determine costing
- Data collection - gather survey data on site
- Pre & post processing - Processing data and preparing the final survey output
- Data quality check - Internal quality assurance by a senior member of the staff
- Project handover - delivery of the final survey output to the client
Topographic Accuracy Standards
Assignment 1: Topo survey/mapping standards in Kenya?
End of Lecture
Topographic Mapping
That's it!
Queries about this Session, please send them to:
*References*
- American Society of Civil Engineers, 2000
- The surveying handbook. 2nd Edition. Springer, 1995,
Brinker, R. C. and Minnick, R.- Kenya Survey Manual
SOK- Land Surveyor Reference Manual
Andrew L. Harbin
Courtesy of Open School